<ol id="33bym"></ol> 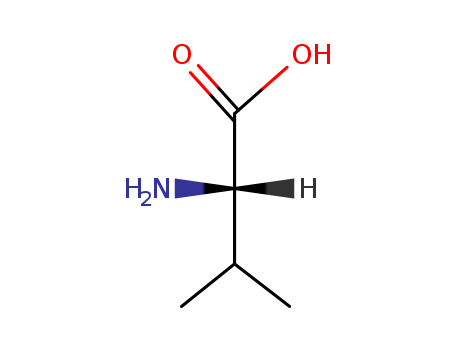

Contact Us: +86-15508631887(WhatsApp/WeChat)
Email:sales@finerchem.com
|
Industrial Applications |
Description: Valine (L-valine) is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) widely applied in various industrial fields such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and feed. |
|
Biological Importance |
Role in Muscle Tissue Recovery and Repair: Valine aids in muscle tissue recovery and repair, as well as increasing energy and endurance. |
|
Medical and Nutritional Uses |
Inhibition of Tissue Protein Degradation: Valine can inhibit the degradation of tissue proteins, improving the carcass quality of livestock and poultry. |
|
Production Methods |
Microbial Fermentation: Currently, microbial fermentation is the primary method for producing L-valine, with mutagenesis and metabolic engineering strategies employed to enhance production. |
|
General Description |
Here is a concise paragraph summarizing L-Valine based on the provided abstracts: **L-Valine** is a branched-chain essential amino acid with the chemical formula (2S)-2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid. It serves as a key building block in peptide synthesis, as demonstrated in studies involving stable peptide helices, enzyme inhibitors (e.g., human leukocyte elastase), and chiral catalysts for asymmetric reactions. Its incorporation into peptides influences secondary structures, such as 310-helices, and enhances stereoselectivity in organocatalysis. Additionally, L-Valine derivatives are utilized in prodrug design (e.g., naproxen conjugates) and chemoenzymatic synthesis (e.g., 4-amino-2-hydroxy acids), highlighting its versatility in medicinal chemistry and biocatalysis. *(Note: The paragraph synthesizes relevant findings while excluding direct references to the literature itself.)* |
InChI:InChI:1S/C5H11NO2/c1-3(2)4(6)5(7)8/h3-4H,6H2,1-2H3,(H,7,8)
Fungal natural products play a prominent...
Surfactins are natural biosurfactants wi...
Carboxypeptidases enzymatically cleave t...
Inherently chiral dialkyloxy-calix[4]are...
C28H41N5O10

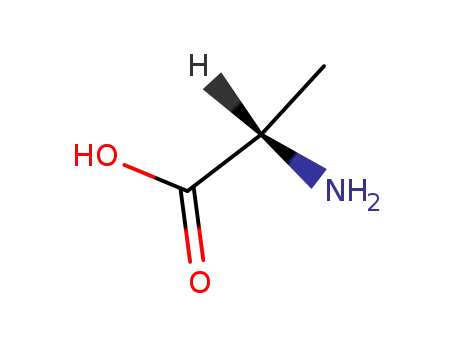
L-alanin
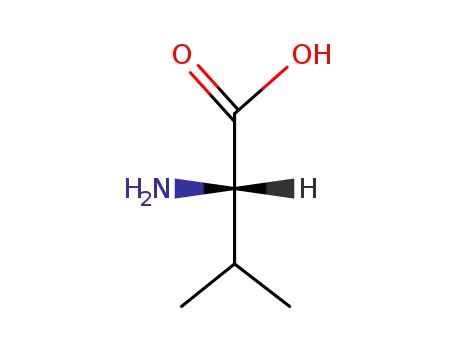
L-valine

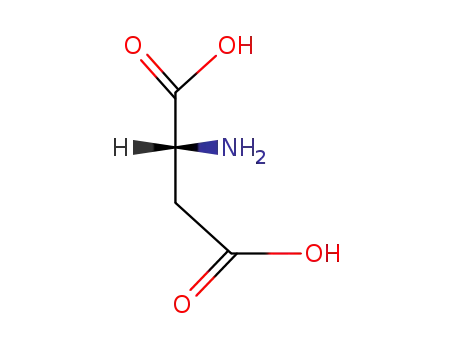
(2R)-aspartic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; water;
at 120 ℃;
for 14h;
|
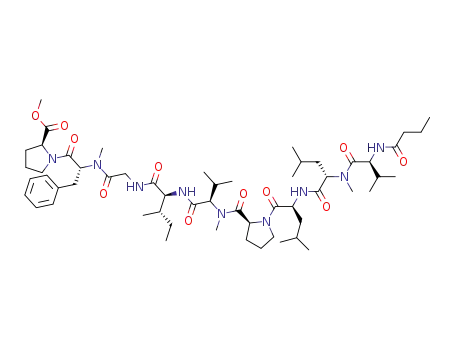
amantamide


L-valine

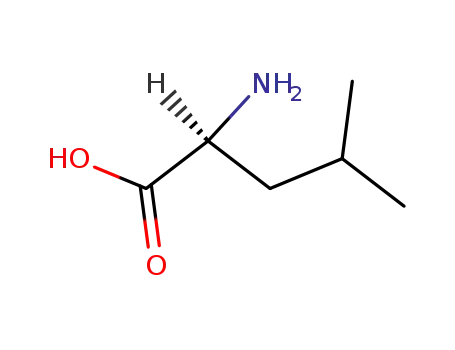
L-leucine

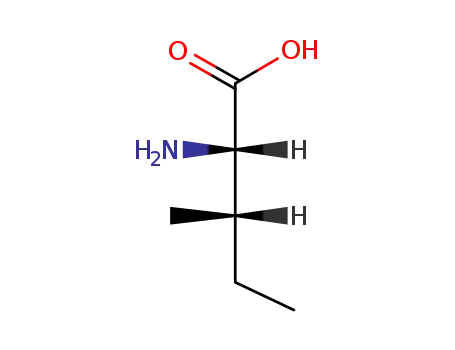
L-isoleucine

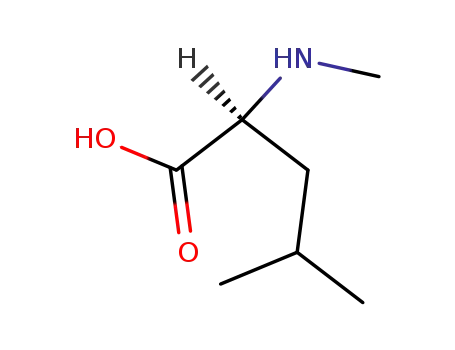
N-methyl-L-leucine

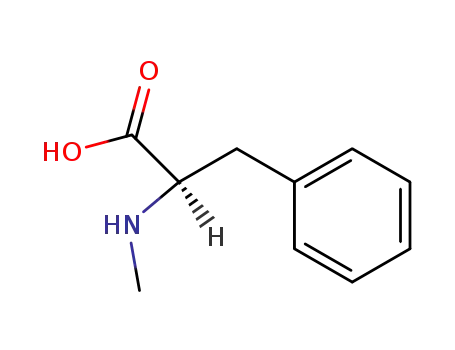
N-methyl-D-phenylalanine

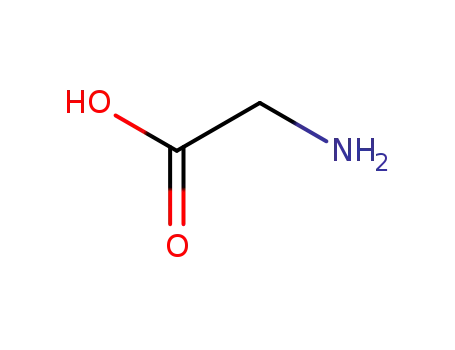
glycine

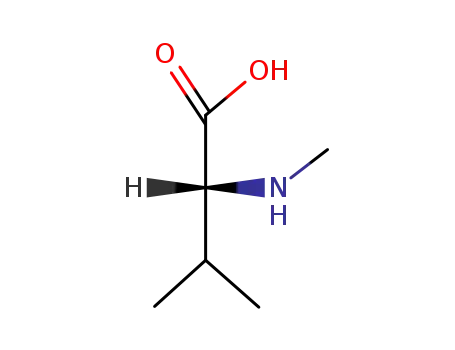
(-)-α-methylamino-β-methylbutyric acid

L-proline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride;
In
water;
at 110 ℃;
for 24h;
|
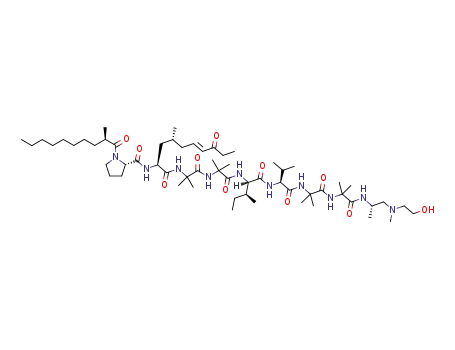
trichoderin A1
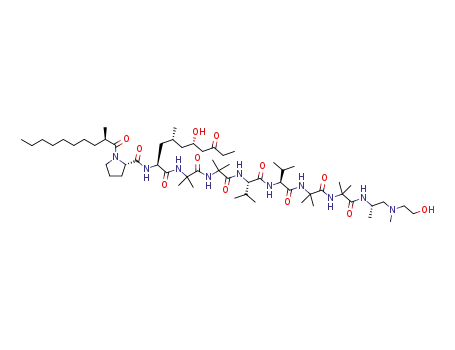
trichoderin B
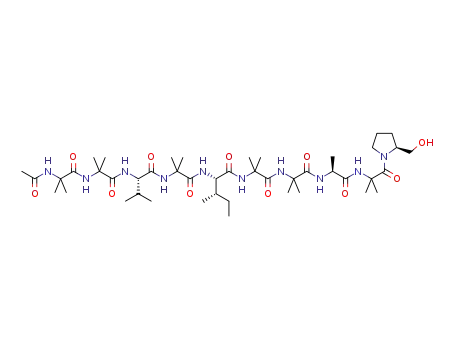
aspereline A
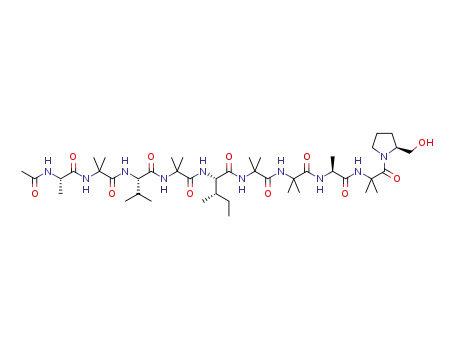
aspereline B
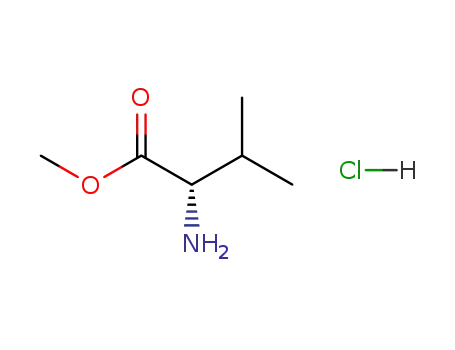
L-valine methylester hydrochloride
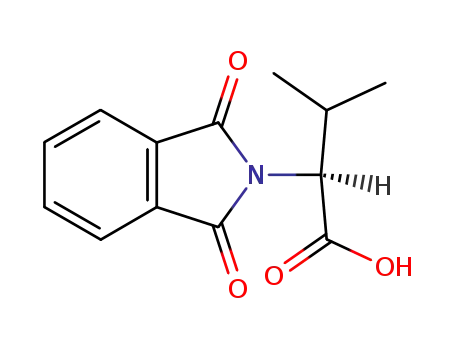
N-phthaloyl L-valine
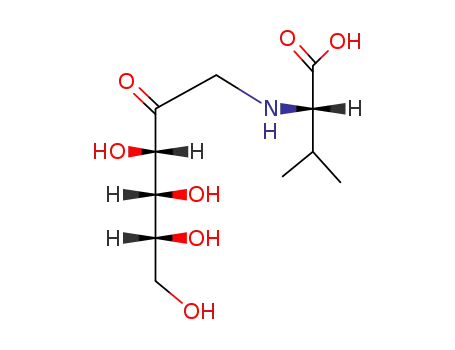
N-(1-deoxy-D-fructos-1-yl)-L-valine
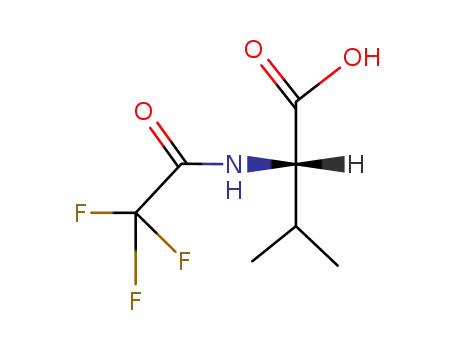
N-trifluoroacetyl-L-valine
