<ol id="33bym"></ol> 

Contact Us: +86-15508631887(WhatsApp/WeChat)
Email:sales@finerchem.com
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
|
Environmental Fate |
Routes and pathways relevant physicochemical properties (e.g., solubility, Pow, Henry constant.)consumer and industrial items and play an important role in safeguarding life and property. A large and diverse group of anthropogenic compounds constitute flame retardants, which are added to combustible materials to render them more resistant to ignition. They are designed to minimize the risk of a fire in the event of contact with a small heat source such as a cigarette. A wide range of different flame retardants is produced, because many materials and products that are to be rendered fire safe are very different in nature and composition. Therefore, having variety in flame retardant products is necessary so as to retain key material functionality. For example, plastics have a wide range of mechanical and chemical properties and differ in combustion behavior. These materials in particular are the main focus of phosphate ester flame retardants.Phosphate esters are derivatives of tri protic acid, phosphoric acid, with a general formula of RxH3°xPO4. Flame retardants are composed of a group of chemicals with similar properties but slightly different structures. They are typically liquids and some are solids at room temperature. Some examples of the phosphate ester flame retardants include: tris(2-chloroethyl)phosphate (TCEP), tributyl phosphate (TnBP), tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate (TBEP), tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCP), triphenyl phosphate (TPP), tris(2-chloro-isopropyl) phosphate (TCPP), and triisobutyl phosphate (TiBP). These compounds are trisubstituted and categorized as alkyl (TnBP, TiBP), alkyl ether (TBEP), chloroalkyl (TCEP, TCPP, TDCP), and aryl (TPP) phosphate esters. |
|
Purification Methods |
Purify it by repeated crystallisation, from hexane, of its addition compound with uranyl nitrate. (see tributyl phosphate.) [Siddall J Am Chem Soc 81 4176 1959; see Cherbuliez in Organo Phosphorus Compounds (Kosolapoff & Maier eds) Wiley Vol 6 pp 211-577 1973.] |
InChI:InChI=1/C12H27O4P/c1-10(2)7-14-17(13,15-8-11(3)4)16-9-12(5)6/h10-12H,7-9H2,1-6H3
This paper presents measurements on the ...
The "third phase" formation phenomenon i...
Due to obtain trialkylphosphate is sugge...
The novel eco-efficient methods to trans...
Oxidative alkoxylation of Zn3P2 with the...

copper phosphide
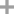
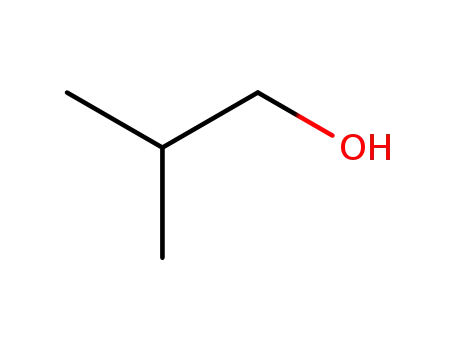
2-methyl-propan-1-ol

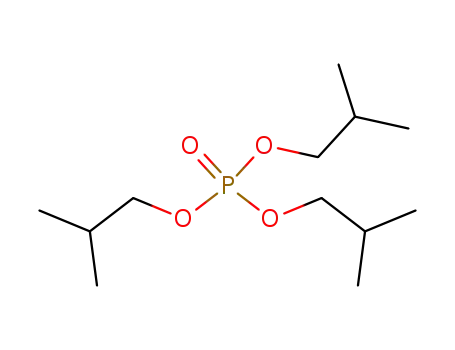
triisobutyl phosphate

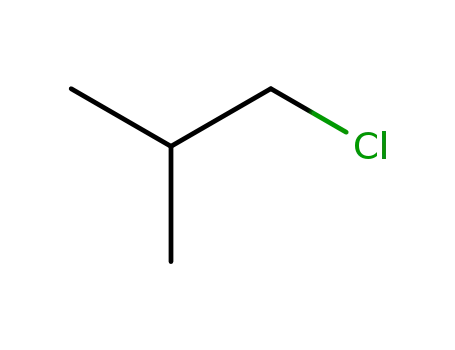
isobutyryl chloride

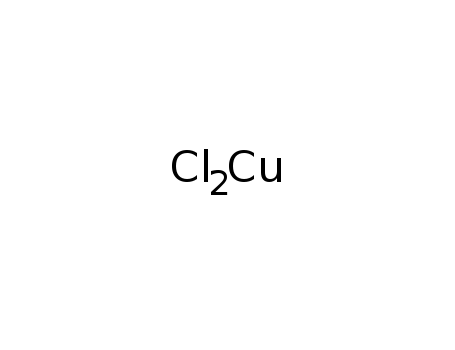
copper dichloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
O2; CuCl2;
In
neat (no solvent);
byproducts: H2O, HCl; the alcohol was loaded together with CuCl2 into the reactor and purged with an Ar-O2 mixture; then Cu3P was added and the mixt. reacted at 293 K, 323 K or 343 K;;
Kinetics;
|
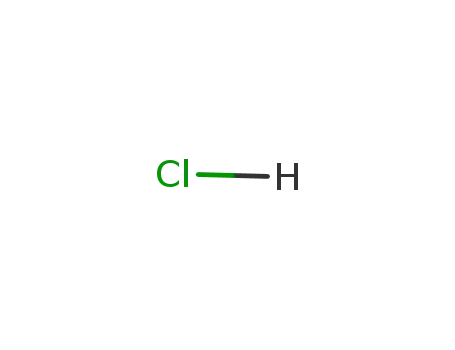
hydrogenchloride

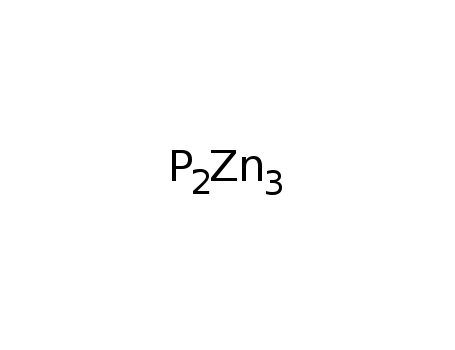
zinc(II) phosphide


2-methyl-propan-1-ol

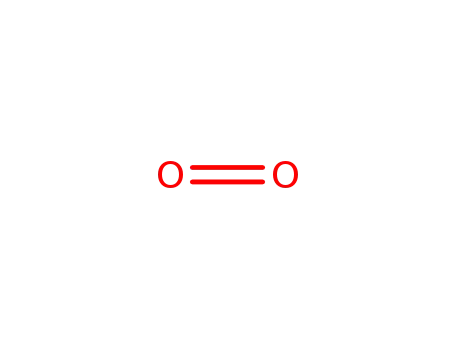
oxygen

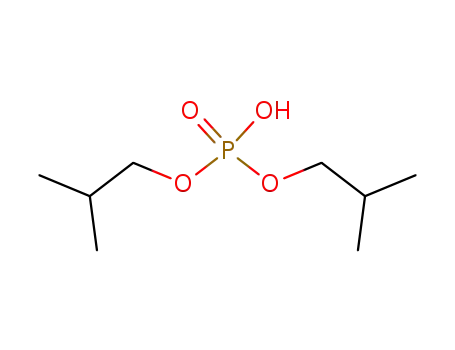
diisobutyl phosphoric acid


triisobutyl phosphate


isobutyryl chloride

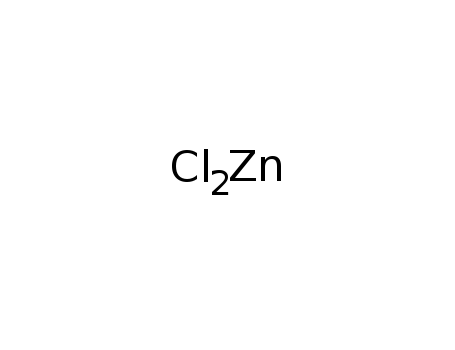
zinc(II) chloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
copper dichloride;
In
further solvent(s);
Kinetics;
|

2-methyl-propan-1-ol
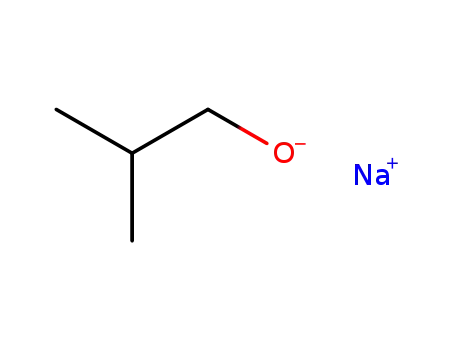
sodium isobutoxide
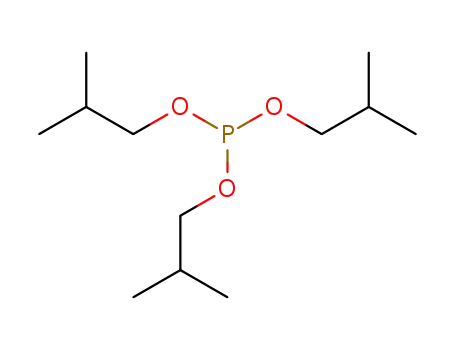
triisobutyl phosphite
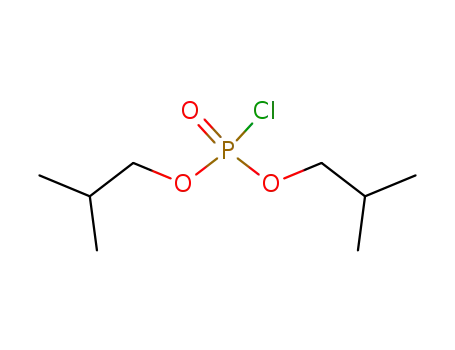
phosphorochloridic acid diisobutyl ester
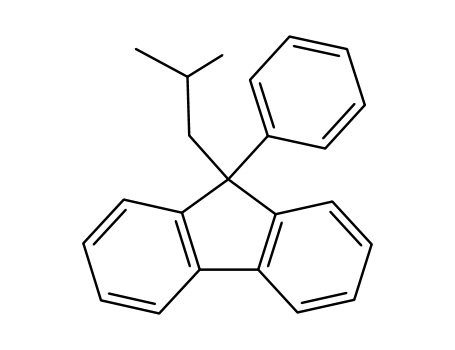
9-Isobutyl-9-phenyl-fluoren
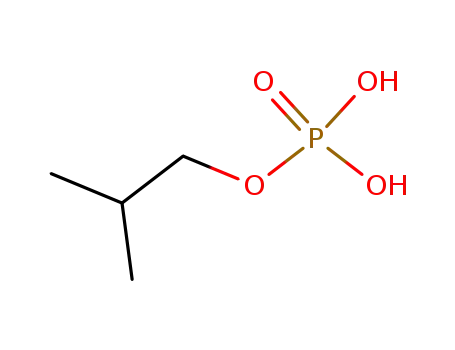
Phosphorsaeure-sec.-butylester

diisobutyl phosphoric acid
5-Chloroisatoic anhydride
